Robert Triggs / Android Authority
ChatGPT has become an indispensable creative tool for many of us. Cutting-edge as it is, however, ChatGPT still suffers from occasional slowdowns that can leave you waiting for seconds or even upwards of a minute between responses. Switching to the paid ChatGPT-4 model won’t necessarily speed things up either. All of this begs two important questions: why is ChatGPT so slow and what can we do to improve it?
Why is ChatGPT so slow? A technical overview
Calvin Wankhede / Android Authority
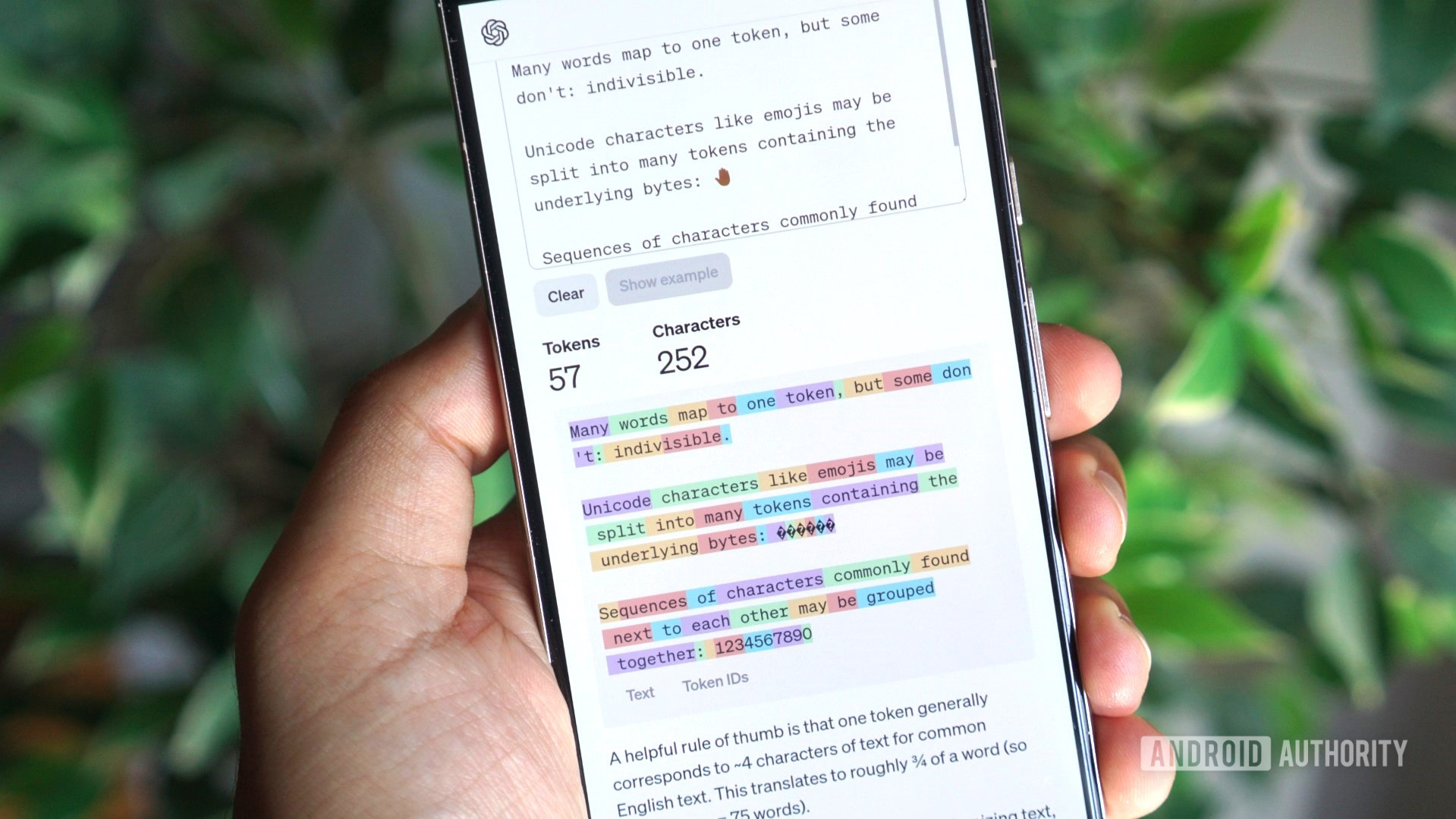
ChatGPT is an example of generative AI, or artificial intelligence that can generate new content. It’s a process that requires significant amounts of computational power. Each time you send the chatbot a message, it needs to decode it and generate a new response. Internally, ChatGPT’s underlying language model processes text as tokens instead of words. You can think of a ChatGPT token as the most fundamental unit of the chatbot’s message.
Language models like the one powering ChatGPT have been trained on hundreds of gigabytes of text, meaning they’ve learned the patterns of human language and dialogue. Given large volumes of text, it can also learn context and how words and sentences relate to each other. Using this training, we can then ask the model to generate entirely brand-new text that it has never seen before.
ChatGPT’s underlying tech requires large amounts of (limited) computing power.
So each time you ask ChatGPT something, the underlying model leans on its training to predict the next word or token in its response. The model can sequence these probability calculations to form entire sentences and paragraphs of text.
Each token prediction requires some amount of computational power, just like how our brains can sometimes pause to make decisions. The only difference is that AI models running on powerful servers can typically predict hundreds of tokens every second.
As for what makes ChatGPT so slow, it’s simply a matter of excessive demand for the limited amount of computational power available. The language model you pick has an impact too — more advanced models are generally slower. While OpenAI hasn’t released exact numbers, it’s safe to assume that GPT-4 Turbo will not respond as quickly as the standard GPT-3.5 model.
ChatGPT-4 is slow because it uses the slower GPT-4 Turbo model, which prioritizes response accuracy and quality over speed. The regular ChatGPT or GPT-3.5 model has received incremental updates for well over a year at this point, making it much faster but less accurate.
How to improve ChatGPT’s response speed
With the explanation of how ChatGPT’s responses work out of the way, you might be wondering if there’s a way to speed up its responses. Luckily, there are a few things you can try to improve the situation.
1. Try a different browser, connection, and device
Before assigning the blame squarely on ChatGPT, we should try and rule out any potential reasons for the slowdown on our end. A misconfigured browser or internet connection could just as easily be the reason behind slow ChatGPT responses, so it’s worth starting there.
Before proceeding, we’d recommend clearing your browser’s saved cookies and cache files. To do this, head into your browser’s settings page and look for a reset or clear browsing data button. In Chrome, for example, it’s under Settings > Reset > Restore settings to their original defaults > Reset settings. After resetting your browser, you’ll have to log into your ChatGPT account again.
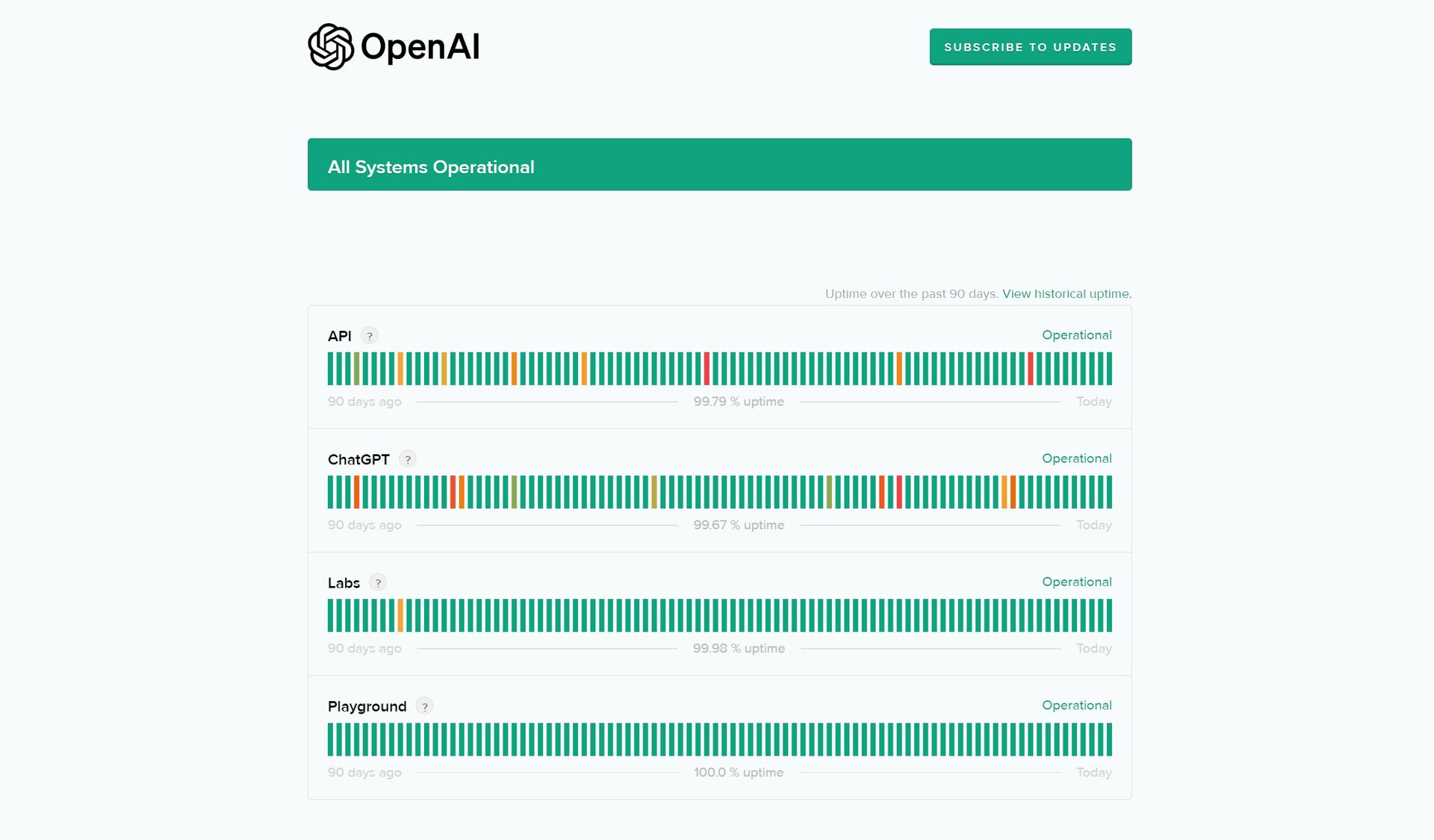
2. Is ChatGPT slow today? Check OpenAI’s status page
Calvin Wankhede / Android Authority
OpenAI maintains an official status page that can tell you if ChatGPT is not working or experiencing slowdowns at the moment. It’s the quickest way to know whether the service is affected by a major outage or has difficulty keeping up with increased user demand.
If the status page indicates an issue with ChatGPT, there’s unfortunately nothing you can do to fix it. Most issues are resolved within a few hours, so you may not have to wait very long.
3. Check for an active VPN connection
While a VPN on its own doesn’t necessarily translate to slower ChatGPT responses, corporate or public ones may affect the chatbot in subtle ways. Corporate VPNs, in particular, may block or interfere with the connection to ChatGPT’s servers.
Likewise, if you use a popular VPN service and connect to a busy server, ChatGPT’s servers may detect a flood of requests from a single IP address. This could trigger anti-spam measures or rate limiting, which throttles the speed at which you can send and receive messages.
The best course of action would be to try using the chatbot without a VPN connection if you currently have one enabled. We already know that ChatGPT saves your data at the account level, so there’s no privacy benefit to using a VPN here.
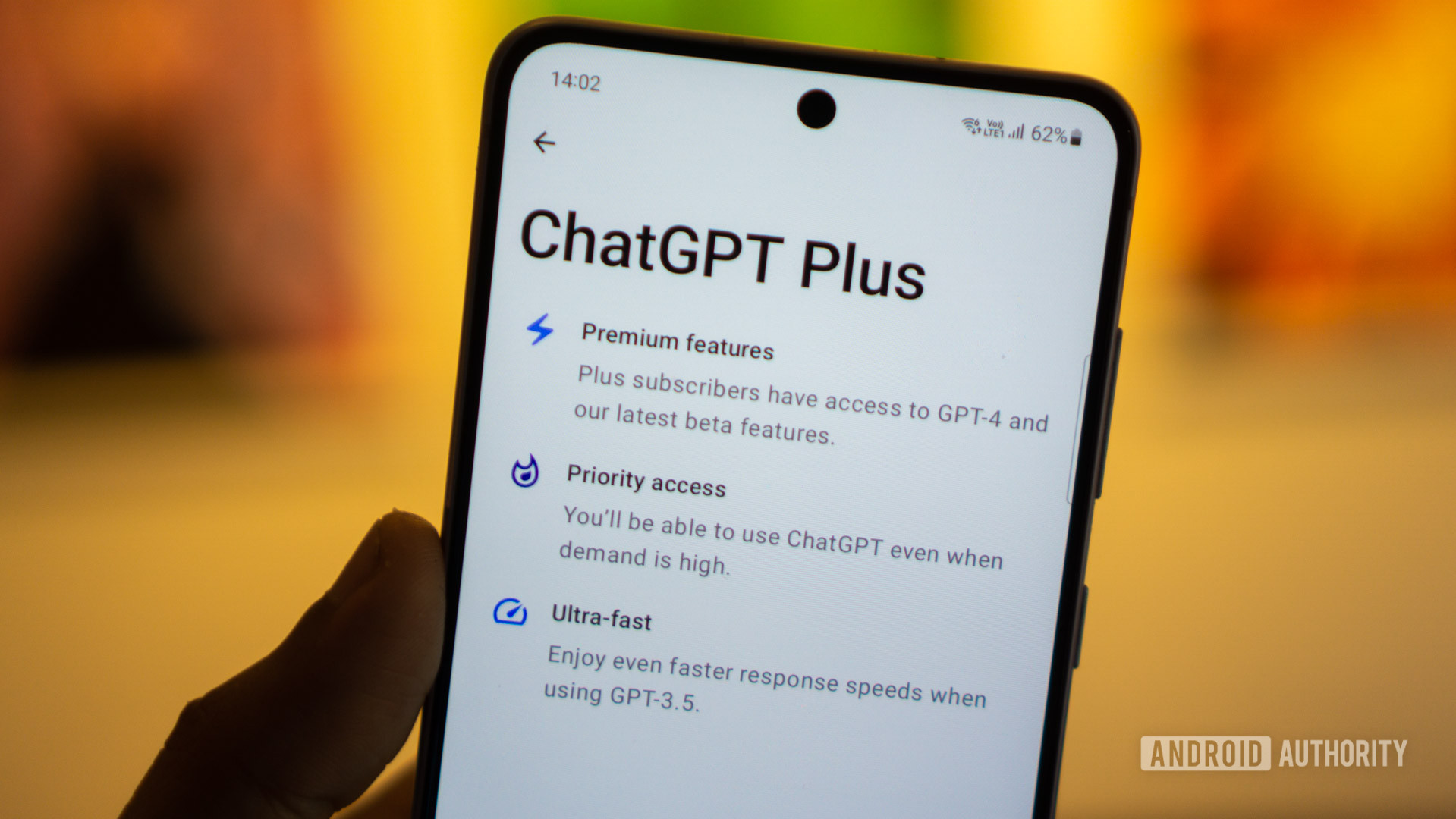
4. Upgrade to ChatGPT Plus
Calvin Wankhede / Android Authority
If none of the previous solutions worked for you, it may be because you tend to use ChatGPT when it’s at its busiest. And if you use the chatbot for free, you’ll be lower on the priority list compared to a paying customer. If response speed truly matters to you, a ChatGPT Plus subscription might be your last resort, although you should consider reading the next section first.
A ChatGPT Plus subscription will set you back $20 monthly but it does offer faster responses. You also get priority access to the chatbot during periods of heavy demand, which should help with any slowdowns you may face.
5. Use an alternative chatbot with faster response times
Calvin Wankhede / Android Authority
While ChatGPT was once the only AI language tool on the market, that’s no longer the case. Take Microsoft Copilot, for example. Even though it relies on the same GPT family of language models, it may have a speed advantage depending on ChatGPT’s server load. But in my experience, Google’s Gemini typically delivers faster responses than either GPT-based chatbot.
Likewise, a handful of other generative AI-based tools like Perplexity offer faster responses than ChatGPT. This is likely because conventional chatbots need to remember previous messages for context, which can increase the complexity of token predictions. Smaller language models will also deliver faster responses but at the expense of response quality.








